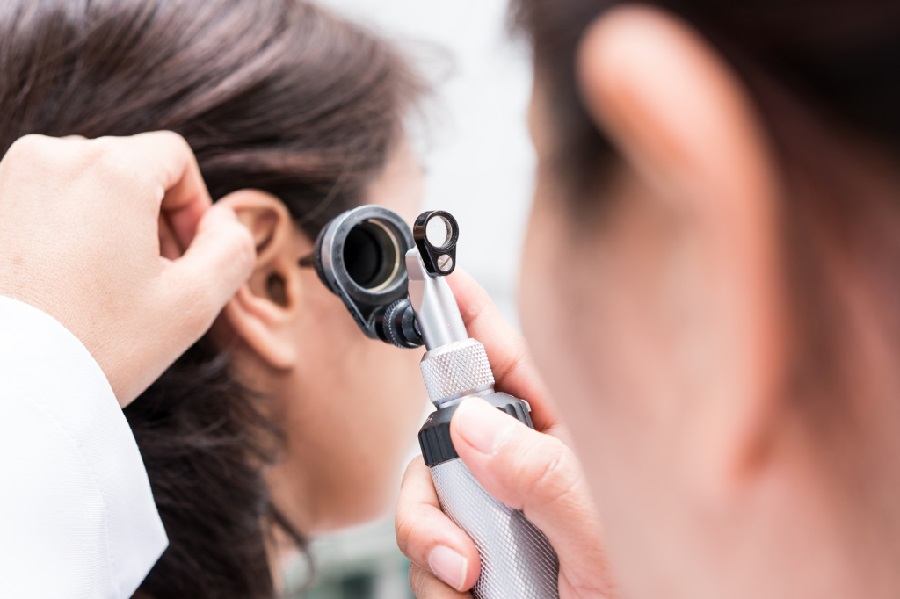
The most common type of hearing loss is age-related, or presbycusis. This condition occurs when our ears lose their ability to focus on sound. The outer ear and middle ear become less sensitive to sounds as we age, which can make it harder for us to understand speech in noisy environments. Get in touch with us related to Hearing aids in Ear wax removal worcester
Other types of hearing loss include:
Sensorineural hearing loss: This type of hearing loss occurs when the hair cells in your inner ear die or become damaged by loud noises. Sensorineural hearing loss can be temporary or permanent and comes with its own unique set of symptoms.
Congenital deafness: This type of deafness is present at birth and cannot be cured with surgery or medication; however, it may improve over time with treatment if it’s caught early enough. Congenital deafness usually affects one ear only but can affect both ears in some cases.
There are many different types of hearing loss. The most common ones are sensorineural hearing loss and conductive hearing loss.
Sensory Hearing Loss
Sensory hearing loss occurs when the hair cells in your inner ear get damaged or destroyed. This causes a loss of sensitivity to sound waves traveling through the ear canal. It can be caused by an infection, trauma or disease.
Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss occurs when there’s an electrical problem that affects the middle ear bones and muscles. This type of hearing loss is caused by damage to the cochlea (the part of your inner ear responsible for processing sound) due to noise exposure (such as loud concerts), age-related changes or autoimmune disease such as lupus erythematosus (lupus).
There are many different types of hearing loss. The most common types are sensorineural hearing loss and conductive hearing loss.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss occurs when the inner ear doesn’t receive enough stimulation from sound waves. It’s often caused by damage to the round window membrane and/or hair cells that convert sound energy into electrical signals in the brain. Sensorineural hearing loss is permanent and cannot be cured or treated with medicine or surgery.
Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss occurs when there isn’t enough pressure in the middle ear (the space behind your eardrum). In some cases, this can be caused by a hole in your eardrum or cataracts (cloudiness in the lens of your eye). Conductive hearing loss is temporary and can be treated with medication or surgery
Hearing loss can be caused by many different things, including aging, noise exposure and genetics.
There are several types of hearing loss:
Sensorineural hearing loss: This type of hearing loss is the result of damage to the nerve cells in your inner ear. The most common cause of sensorineural hearing loss is an infection or inflammation in your middle ear. Other causes include autoimmune diseases (such as lupus) and certain medications such as aspirin or NSAIDs (aspirin-like drugs).
Central auditory processing disorder (CAPD): CAPD occurs when there’s an issue with how sound waves enter your brain and how they are processed. This can cause problems with speech understanding and listening comprehension. Common symptoms include difficulty following conversations, difficulty understanding what people say, trouble understanding directions from others because they’re unclear or hard to understand, and having trouble distinguishing between similar sounds like “s” and “z.”
Hearing loss is a disease that can affect your ability to hear. It’s not the same as having a hearing problem. Hearing loss affects people of all ages and backgrounds.
There are many different types of hearing loss and each one has a different cause, severity and treatment. Most people with hearing loss have tinnitus (ringing in the ears) as well.
Types of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can be classified into three main categories: conductive hearing loss, sensorineural hearing loss and mixed type (where both conditions coexist).
Conductive Hearing Loss: Conductive hearing loss occurs when there is an inability for sound waves to travel through the outer ear canal to reach the inner ear via hair cells or semicircular canals (or both). This type cannot be repaired by surgery alone because it involves damage to nerve cells located within the inner ear itself. In most cases this type of hearing loss will progress over time unless treated early on; however, there are some therapies available that may reduce its impact over time if used correctly by your doctor
Hearing loss is a common condition that affects one in five Americans. It can affect people at any age, but it most often occurs in older adults.
Hearing loss can be caused by a number of factors, including:
Alcohol abuse. Alcohol consumption can damage your ears over time, causing hearing loss and tinnitus (a constant ringing or buzzing in the ears). The more you drink, the greater your risk of developing hearing loss.
Age-related hearing loss (presbycusis). As people age, they lose some hearing ability because their earwax becomes less fluid and sticky so it doesn’t seal as well as it once did. This may result in reduced sound sensitivity and an inability to hear high-pitched noises such as birds chirping or fireworks exploding overhead.
Exposure to loud noises like those from gunfire, explosions and heavy machinery. Exposure to loud noises increases your risk of suffering noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL), which occurs when there is damage to the inner ear’s nerve cells caused by exposure to sudden or repeated loud noises such as gunfire or explosions that exceed 85 decibels (dB).